The famous (misquotation) of “reports of my demise have been greatly exaggerated” comes to mind when speaking to Boeing. The Super Hornet is certainly undergoing a rough patch, with the SECNAV Carlos Del Toro trying to kill off the plans to keep building brand-new Super Hornets in the next few years, and instead wanting to focus on the F-35C (and to a lesser extent F-35B) which was described as “a far more significantly capable aircraft”. This is something of different message compared to the earlier one which has been making rounds, where people such as the US Navy’s chief of the naval operation’s air warfare directorate, Rear Adm. Andrew Loiselle, have expressed that he would prefer to focus more on the mid-life update (Block III) instead of on new-builds because any new-built Super Hornet with their 10,000 hour airframe will fly past 2055, and they don’t see “a lot of analysis out there that supports fourth-generation viability against any threat in that timeframe“.
Boeing readily admits neither message is particularly helpful for their export campaigns.
However, one has to give Boeing a point in that it is clear that at least some of the messaging is clearly directed a result of domestic politics. The US Navy has been struggling to fit all of its priorities into a defence budget that is flat or potentially even falling, with new classes of submarines and destroyers (to replace both early Arleigh Burkes as well as the Ticonderoga-class cruisers) competing with the Super Hornet-replacement-to-be NGAD for funds. The risk of a delay to NGAD is obvious, especially as the force struggles with how to close a “fighter gap” and the house having thrown out the latest set of USN calculations this summer (this is part of a rather longstanding pattern of the politicians not trusting the US Navy to make sound long-term planning decisions and run projects efficiently, which unfortunately isn’t completely unfounded). At the same time, it is rather obvious that some of the Super Hornet’s greatest friends on the hill are representing Boeing-strongholds and might not be guided solely by strategic insights…
Regardless of the outcome, the stated goal of replacing the Super Hornet during the 2030’s does seem optimistic considering the reported state of the NGAD. Crucially, for the time being there also doesn’t seem to be a plan for how to replace the EA-18G Growler with its unique set of capabilities (this is the place where visionaries usually throws in a slide showing a bunch of networked unmanned platforms shooting lightning-shaped datalinks and electronic attack effects between allied forces and against enemies respectively like a latter-day Zeus, but I would again like to state my scepticism of there actually being something resembling a practical plan buried in those slides. The USMC has something a bit more real in the works, but so far that doesn’t include a true Growler-replacement either).

But what is really interesting is the second wind of export interest in the aircraft. Granted Canada apparently has kicked out the fighter (though it has to be said it hasn’t been particularly well-loved north of the border after Boeing dragged Canadian aerospace company Bombardier to court over their jetliners), but the German Super Hornet/Growler-buy seems to have survived the change in government and is reportedly moving forward, and as is well-known there is a strong push to try and get the Indian Navy to see the light and acquire the Super Hornet for their carrier operations. More interesting was Boeing disclosing that they are in talks with Spain about the Super Hornet (almost certainly related to the same EF-18A/B Hornet and EAV-8B Matador/Harrier II as the recently revealed F-35 discussions), as well as stating that the UK have expressed interest in Super Hornet STOBAR testing conducted for the Indian Navy efforts (and where this testing could lead). Notable is that the flight deck of the Queen Elizabeth-class compares rather well with that of the the INS Vikramaditya when it comes to length and area (though the designs obviously differ), and while it isn’t angled, the Juan Carlos I with its 201.9 m long and 32 m wide flight deck actually matches the 198 m long and 30 m wide angled recovery deck and 195 m long take-off run of the INS Vikramaditya. Speculations about a STOBAR-carrier in Spanish service may hereby commence (though I will warn you that the step from discussing the theoretical possibility to actually converting the vessel is a rather drastic one).
Regardless, there is a non-trivial risk that any Finnish Super Hornets will be the last new-built rhinos rolling off the production line, and the Finnish Air Force has been strongly stating the importance of being aligned with the main user (to the extent that the Swedish Air Force threw out their own long-term planning and instead adopted the Finnish set of requirements in order to ensure that the JAS 39E remained a viable alternative). So how is Boeing intending to work around this issue?
To begin with, while the Super Hornet likely will bow out of USN service before the Finnish Air Force retire HX, as mentioned the Growler will likely soldier on for a bit longer (again, compare the A-6 Intruder retiring 22 years before the EA-6B Prowler), allowing for updates made to keep that platform modern to support exported Super Hornets. The German order is also a key piece of the puzzle (I mean, does anyone really think that the Germans will retire any platform acquired before having worn it down? We are after all talking about the country that flew F-4F Phantoms in central Europe until 2013).
But the big news is the Open Mission Systems, which allows for what Boeing describes as containerised software. Behind the jargon lies a principle through which the software is written once, put into a so called fusion app (the ‘container’ in ‘containerised software’), which then allows it to be pushed out to a number of platforms – manned, unmanned, fixed-wing, rotary, you name it – simultaneously through making the software hardware (and even manufacturer) agnostic.
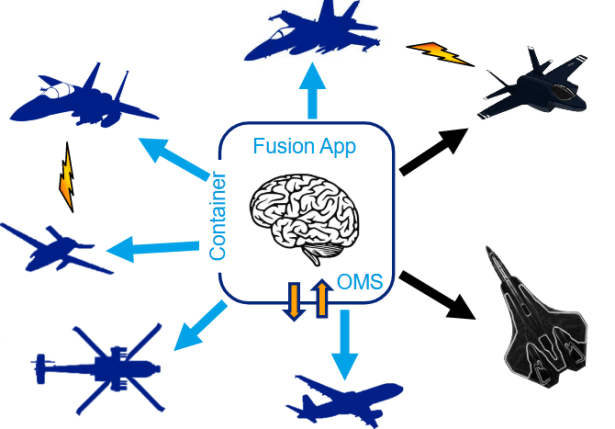
While the principle is significantly easier to implement on a PowerPoint-slide than in real-life, successful lab testing with containerised fusion algorithms in the F/A-18 Block III and the F-15EX has taken place, and plans are progressing for flight demonstrations. If the program develops as expected, it would provide the opportunity to piggy-back F/A-18E development onto that of e.g. the F-15E(X), which would grow the user base and spread development costs significantly.
But it’s not just the aircraft itself that are easily upgradable. Michael Paul of Raytheon Intelligence & Space is happy to explain how the NGJ-MB pods are not only cutting-edge today, but that their open design ensure they will stay that way.
The current ALQ-99 jammers made their combat debut in Vietnam, and although it has undergone numerous upgrades and still is a competent system according to most accounts, there’s no denying that it’s greatest days are already behind. The new family of jammers, the mid-band unit of which will be first one out and which passed Milestone C (current version accepted as production standard) earlier this summer, will bring a serious improvement. Trying to find a suitable comparison, Paul struggles a bit. “It’s a level above going from mechanically scanned radars to AESA-technology,” he explains. “It’s a significant leap just because of its AESA-technology, but then you add the power.”

And while having an AESA-array means that you can do all sort of nice stuff – both Lockheed Martin and BAES are pushing the fact that they are doing some serious electronic warfare stuff with their arrays – the power and dedicated subsystem really takes things to another level. While a modern AESA-radar for a fighter can give self-protection at levels earlier only dedicated platforms could provide, it is still very much a case of self-protection. Because the dedicated platforms have also stepped up their game. The fact that the NGJ isn’t just a Naval program but sorting under joint oversight in the DoD structure speaks volumes as to the importance the Pentagon places on the program, even while at the same time discussing the need for fifth generation aircraft (the push to integrate the pod on USAF fighters is another datapoint). The NGJ allow the Growler to do what Raytheon describe as “force-level protection”, and while the exact capabilities of the pod are classified, it is significant to note that the Pentagon has been placing an ever increased importance on the electro-magnetic spectrum (EMS), and being able to treat it in the same way as other more familiar terrain – doing manoeuvres and conducting fires in it, so to speak.
This is what modern day air operations looks like
Achieving EMS-superiority will be a key mission for any air force in the future, and the Growler is well-poised to support any force attempting to do so.
What the design of the pod brings with its increased power output is the ability to handle wider spectrums and go straight to the key nodes, which in an integrated air defence systems might or might not be the shooter – it might as well be a surveillance system standing way back, feeding information to silent SAM-batteries operating missiles with their own guidance systems (active radar or IIR). But while the pod is great, the integration of the two-pod shipset with the mission systems of the aircraft really is where the magic happens. The “incredibly integrated” nature of the shipset means that the Growler and the pods are sharing data back forth, including from their own sensors but also from third-party sources (including via satellite), together creating the situational awareness that the Growler is known for, the “I know everything”-feeling as 9-year Growler veteran (and Prowler before that) Michael Paul puts it. The location of the arrays on the pods also means that the aircraft is able to cover the strikes throughout their mission – either from stand-off ranges or as penetrating platforms.

While the days of the Super Hornet might be numbered, no one quite seem to know the exact number for sure. It also has to be remembered that many of the particular drawbacks quoted by the US Navy center on how it would like to operate in a China-scenario. The situation in Finland is markedly different in a number of ways, including the significantly lower emphasis placed on range. The very real risk of losing support from the main user toward the last decade or two of the aircraft’s career is no doubt a significant drawback, but at the same time the offer here and now would fit the Finnish Air Force extremely well both as a capability but also in the FDF’s general culture of being somewhat risk averse and preferring mature systems and a continuous iterative development rather than radical steps. And as icing on the cake comes the Growler, which not only would be a strategic assets for both the political and military leadership throughout the span from peace through crisis and into war, but also a huge political signal of the close bond between Finland and the US.
As Paul noted:
It likely wouldn’t have been possible to offer this ten years ago.


Re Growler and its value.
Modern fire control systems (Air to Air, Ground to Air) are so effective when undisturbed that it’s murder to fly against them if unjammed. Stealth shortens the effective range, but a VHF radar has about 150km range on a frontal (=best) sector F-35, so the position is no secret without background EA.
If you study the Cosvo situation where an F-117 was shot down, theater jamming (the class Growler or Gripen EW + EA pod does) was at hand. In fact, no stealth aircraft has flown into a modern fire control system without background jamming to support. It’s a >$100m+ asset and you don’t risk it on those premises.
For EA, the airframe platform requirements take a backseat to EA performance, thus Growler’s longevity.
Re EA effectiveness, in addition to AESA, the latest systems add another vital difference (you should perhaps have been in the business to understand this, I’ve written about it before). Until the last 10 years, EW and Radars had to have a thick layer of RF hardware (tuners, oscillators, filters…) behind a receive/transmit antenna. This makes it a stale system that can only evolve with slow and costly hardware upgrades, typical at mid-life. With the arrival of high-speed ADC/DAC (in the many GigaSample range for Analog to Digital Conversion and vice versa) no more.
You directly sample/generate the RF signal to/from wave-form analyzing/generating software just before the antenna. The only RF layer is the first/last amplifier stages and a frequency folding LO step. What it all enables is Radars/EW systems that are software-defined (we’ve had it for COMs for some time). Now you can keep the system relevant for decades with software changes.
More importantly, you always fight the last war on the first days of operation. With software-defined systems AND an agile software architecture, you can adapt immediately. The winner will be the force with the thinnest RF layers combined with the most agile software architecture+teams.
The NGJ mid and low band pods as well as Gripen’s EW + EA pod are of this generation, the ALQ-99 represents the old stuff. This is why it’s such an important upgrade. it’s not only that it goes from MSA to AESA.
As an ex. fighter pilot, it hurts that our skill in “knife-fighting in a telephone booth” is becoming less relevant and that my software team will save my bacon. But as we’ve seen in the recent Gulf and Nagorno-Karabakh conflicts, those that fight the last war lose (who would have guessed the Turks were SOO good in drones). Advanced EA is an absolute necessity in a future conflict or you lose.
Only the Growler and Gripen EW provide qualified EA in BAFO, others should’ve.
You are wrong.
When the F-117 was shot down the Prowlers was grounded, and the serbs know that the F-117 still would fly. They had spotters and informants in Italy, and they also knew that they used the same path a lot of time. Something they never did during Desert Storm.
Do you realize that you confirm what I said?, i.e. EA unavailable = the stealth machine is shot down?
The AEA pod slated for the Gripen (from the Saab Arexis family) doesn’t seem to have its own power generation system so its transmit power is limited considerably by what a MIL-STD-1760 pylon can deliver (a max of 200 V/24 A cont and 30 A peak). That would restrict it to about half to two thirds of the transmit power of the ALQ-99, and surely quite seriously below what the NGJ pods can put out. That would limit its usefulness for “theatre jamming”, beyond the escort and self protection role.
The Hensoldt Kalaetron family AEA pod (earmarked for a potential (!) German Eurofighter ECR variant is intended to have its own power generation, so that may end up being an NGJ equivalent capability at least in potential transmit power, who knows about frequency coverage or available jamming techniques though. Not sure about the just announced IAI Scorpius or French or Italian options either.
Re EA power:
In EW the antenna is in general more important than other stuff, so also here. The EA power is measured in ERP (jamming power emitted) which is transmit power * antenna gain. Of these transmit power increase is hard (and often not needed) whereas antenna gain is easy, if you have the right receiver angular accuracy and transmit antenna type. Gain and power count equally. In fact, higher antenna gain is more desirable as it means a more focused lobe, you disturb your own surroundings less.
Example to make to prove the point:
Assume an AESA with 48 GaN elements, each giving 15W peak = 720W power (Arexis EA pod, my take). At S-band you have an antenna gain of 79 times (19dB). A good antenna is polarisation agile, rendering an ERP of 56kW (Arexis antennas are polarisation agile).
Now assume a less good antenna that is not polarisation agile but angeled at 45° (as so many are). You lose half the ERP for victim radars with vertical or horizontal polarisation, i.e. you are now at 28kW.
If we don’t have vertical receiver resolution we apply an AESA like the SPECTRA or DASS types, with a +- 45° vertical lobe, directable in azimuth, with 45° polarisation. Now we are at an antenna gain of 10 and an ERP of 7,2kW (neither has S-band AESAs right now, this is just an example).
in the above, we have left the transmit power at 720W, a reasonable figure with GaN elements. Their efficiency makes for a power budget, including losses and pod management, within the 4,800VA you set as limit.
But I’m not sure SAAB stops at a MIL-STD-1760 for their pylons, they can go beyond if they see a need, they make their own pylons. The real limit is the power budget of the Gripen E (and probably the EA pod low band, down to 150Mhz). But 4800VA of external consumption should be in the design E spec from start, so should be no problem.
The Growler ERP is higher (as Raytheon has shown the antennas it’s easy to estimate the ERP there as well), but not outrageously so. Neither has a burn-through distance problem, we talk nm (check it, you have my estimated data above for the Gripen E, assume 1m2 RCS). The weapons used give standoff distances of 10 times these values.
This assumes escort jamming, standoff is often not on as modern radar has effective sidelobe blanking.
In conclusion, the transmit power is perhaps not the key parameter, understanding the antenna system is more important.
Arexis pods have internal power source.
Re EA power, to complete the examples:
The last example I should have included would be where we use fixed sector antennas (used on for instance the F-18E/F IDECM).
Let’s assume a four-sector antenna system with each covering 120° in azimuth and 90° in elevation (we need the overlap in azimuth as these limits denote the half-power limits). Now we have flood-type lobes as this is how we achieve 360° azimuth coverage. Our S-band antenna gain is then around 3 times (5 dB) (IDECM covers S-band).
Let’s assume we use a polarisation agile antenna type (for instance Sinuous), so we don’t have a 50% loss there. The ERP is now in the 2kW class with the same transmitter power as before.
So we have a 28:1 variation in jammer ERP in these examples, yet we haven’t changed the transmitter power. EW systems are to a large degree defined by how pointy the antenna lobes can be, which in turn is defined by the angular resolution of the receiver system positioning the lobes.
The present ECM buzzword is AESA using GaN amplifiers. It promises higher power levels than GaAs (perhaps five times). But equally important is an advanced antenna system, promising 20-30 times in ERP and direct sampling ADC/DACs architecture, so we have a software-defined system.
For the SAAB Arexis on the Gripen E, the buzzword is GaN AESAs as this is easy to communicate. Equally important are the BOR ECM antennas and the use of direct sampling ADC/DACs throughout the system.
Public sources say that F-117 did some sorties over Baghdad without jamming support. I guess those were the happy days of stealth-concept.
Former MoD J.Niinistö hinted that without Growler sales permission, Super Hornet could have been out of the HX competition.
What does a Growler become if you add this pod in it? The Dragon from the book of revelation? The All-Seeing Eye?
“Dragon’s Eye is a powerful sensor system that has an active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar at its core that is capable of being rotated around the pod’s center axis. The pod also contains geo-positioning and cooling systems. The radar has synthetic aperture functionality allowing it to produce high-fidelity imagery of a large area and is said to be sensitive enough to detect small and even shallow-buried objects, such as individual people and improvised explosive devices. It reportedly has ground-moving target indicator (GMTI) capabilities, as well, giving it the ability to track moving vehicles and ships below. What this all means is that system can be used to conduct general intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) missions and collect targeting data for actual strikes, all at extended ranges and in any weather conditions.”
https://www.thedrive.com/the-war-zone/43114/air-force-f-16-carried-dragons-eye-radar-pod-alongside-b-1-bombers-on-red-sea-mission
Seems a bit presumptuous to compare the Gripen E + EJAP to the much more oroven Growler with its new mid & low band pods.I’ve not seen that Saab has provided any data re: it’s new Are is pod.
The containerized software solution sounds exactly what I imagine SAABs gripen E avionics architecture looks like.
The following really is wild amateur guess work but could be interesting for someone. It’s essentially a service centered architecture.
https://ftfsweden.se/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/FT2016_D08_Par_Hammarstrom_GripenE_Avionics_Architecture.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwi2pcPspbj0AhURi8MKHQw_Bq0QFnoECAgQAQ&usg=AOvVaw3J-JGZfAPt8Zx534KH0uTA
check the last 6-7 pages.
(Hardware independent) containers with different responsibilities register the service (incl options) they can provide with a service locator. If they need data from another service they just ask the service locator. The locator basically provides customizable subscriptions to datastreams, at an time interval or at events or possibly some other option. The containers are not aware of anything but the locator. In this way dependencies are kept low.
It really should help with avoiding tight coupling – one of the major problems in many large software projects. The containerization also means that an engineer can run containers on basically any environment. The simulator on your desktop? Sure! The real training simulator? NP! Hardware on your desktop not good enough? Let’s lower the update rate of some services or even make a Mock-service container, np. You could have multiple prototype versions of a container running along side the standard tested verified one during flight. The OSes shouldn’t have any problem handling the mixed criticalities and give highest priority to the flight critical stuff etc. With that said it’s probably super complex in practice. Need layering, lots of automatic tests, ways to make sure that the communication between the containers don’t grow exponentially in a non sustainable maner etc (which could affect the low critical stuff)
I imagine that Boeing/SAAB T7-A does this as well.
I’m by no means an experts so it could be far if the mark, and I’d love to see comments adding information and pointing out fallacies
@Bjorn – you said – if you study the Cosvo situation where an F-117 was shot down, theater jamming (the class Growler or Gripen EW + EA pod does) was at hand.
And I said that this was not at hand at the shot down. I have never said that stealth don’t need jamming.
@corporal
Have you seen this ?
F-35 in Switzerland is well at 110 million dollar/f-35.
Price have risen by 20%
As stated in the DSCA there are only 1 missile par fighter.
How can this have influence on HX ?
https://www.admin.ch/gov/en/start/documentation/media-releases.msg-id-86118.html
May I revisit the issue of runway requirements?
In civilian aviation, it seems that they have various rules for calculating runway requirements and these are NOT the same as the take-off distance for a given plane.
In military use, the rules are probably different. More risk has to be taken in wartime.
In carrier use, these rules are irrelevant.
Let us imagine a scenario where a fighter plane is taking off from a temporary airfield inside a forest. It is carrying a light A2G load and self-defense A2A missiles, and a significant amount of fuel.
Plane starts to move. It is accelerating. Then, somewhere along the runway the pilot decides to reject takeoff for a technical reason. Pilot applies maximum brakes.
Now then, if the runway is not long enough, the plane will hit the spruce trees. Pilot will hopefully eject. Fuel will ignite and weapons load will blow up. This is actually the equal of an air strike on the base.
So you see, it is actually a complex equation. The fuel load and the weapons all affect runway needs, but then there is a million other things too. The military will probably have a system where they calculate risk by statistical methods and then accept different risks for different situations.
Ugh. The weight and drag of those off-set pods…
Whatever Boeing said about CFTs being ‘available for customers’, I suspect that there might be an ‘Oh, did I not mention integration price-tag?’ coming the way of the first user.
Is it out of Canada or not, BTW?
The Finnish range requirements are rather low to be honest, would be surprised if Finland would opt for them (even if the plumbing is included as standard so the option is there).
Conformal fuel tanks is not available for SH. US Navy wanted them for block 3, but they could not be delivered as the technical challenges was to big.
Yes, they are fully integrated. Issue with USN was about safety rules for handling on a carrier deck, i.e. that attachment points used when pushing aircraft overboard were covered, and removing the tanks took too long for the safety standard to be met. Plumbing is there and tanks are available if a customer wants them, though I can’t speak about the price tag.
Hello,
Re- the Indian Navy to equip the INS Vikramaditya, it is to be noted that the F/A 18 is competing with the Rafale M. Not an easy game for F/A 18 given the obvious commonality that a Rafale choice would offer to India with their Air Force, but let see what will happen (when ? That’s always a question with India, you don’t need to be too much in a hurry)
Regarding Spain and the Juan Carlos 1, as you rightly write, I think it’s very unlikely that they would convert their boat in a STOBAR version. However, if they do so, and again if you exclude the F35 for political reasons, the only 2 aircrafts avaliable on the market would be the F/A 18 and the Rafale M (and the Mig 29, but…) In this situation, given the crazy “American buy preference” of the European countries, I think F/A 18 would be the favourite, to the contrary of the Indian market.
In my mind, Indian defence procurement should never be used as an example or benchmark. It seems like their decision making process is entirely based corruption rather than system price/performance.
Why else would they operate so many different aircraft types? Seems like a ungainly and costly way to secure supply by contract dispersal.
India also has the honest-to-God-this-isn’t-a-Rafale HAL TEDBF in the works, though that one might need a stop-gap fighter before it’s ready.
A recent and very interesting compilation of cost data for F-35A usage. LM’s marketing is typical of American companies (spent 1/3 of my career in US companies):
https://www.defense-aerospace.com/article-view/feature/216023/norwegian-defence-budget-reveals-real-f_35-costs-%3Ci%3E%28free-access%29%3C%C2%A7i%3E.html
Probably the most balanced and relevant article I’ve read on the topic of the true actual cost of owning/operating the F-35.
I suspect the crude logic of the US Government is: Every F-35 we sell to a foreign air force is a F-35 we don’t need to buy ourselves.
Let’s just hope they don’t play too dirty this time.
@Svenska Kocken
Balanced? Motivated reasoning stands out like a sore thumb from the article and a dispassionate reader sees through it almost immediately. Its just another round in the same old pissing contest that has been going on for years now. Don’t you guys find it boring already?
@EMK. Look beyond the Briganti article.
The one I referenced is written by Tusa, and more importantly, look at his base figures. These are from the Norwegian Defence budgets. Bogus as well? (BTW, in the spirit of your tone, spare us the rant these are not applicable, yuade, yuade… Come we real arguments). The point is that these are real figures from someone that is actually operating the F-35A outside USAF.
Everyone that has some knowledge knows it’s not very productive to use USAF cost figures for someone that is not operating the aircraft in the USAF manner (their scale of operation for training, operation, maintenance, infrastructure, etc is totally different so thier costs are lower than for an independent operator).
Norway is the closest we get to a Finnish context and these figures are way beyond the LM claims (the ones that are public) for the operation of the aircraft.
Först efteråt såg jag att jag “postat” samma som du ☺️
Well now I can answer both of you at the same time: is it not blatantly obvious which plane is not going to be chosen? Samma på svenska. Men bara några veckor mer
https://www.defense-aerospace.com/article-view/feature/216023/norwegian-defence-budget-reveals-real-f_35-costs-%3Ci%3E%28free-access%29%3C%C2%A7i%3E.html
Look at this. Max 50f35 for FAF. I am not the right guy to break this down, but to me its looking seriuos.
HX program director Lauri Puranen has always said that Finland cannot acquire fighters it cannot afford to operate.
MoD Antti Kaikkonen has lately almost always started HX discussion with 4 fail/pass gates, sometimes emphasizing the operating cost-gate. Lately Kaikkonen has hinted that some providers might not make it through from those gates. I would say that no smoke, without fire.
Latest official defense paper guides, that HX operating cost must take account of military-tech inflation. So operating cost limit is not 250M but actually far lower as otherwise there is no safety marginal or growth marginal for the future.
@Lars Rehnberg
The website defense-aerospace dot com belongs to an individual freelance writer based on France. His/her business name, according to French business registry, is De Briganti, and his/her LinkedIn profile uses pseudonym Giovanni De Briganti, a name of an Italian WW-I fighter pilot who passed away already in the 1930’s. There is no information about his/her background, past activities, aviation related affiliations or anything else that would suggest s/he is an expert in anything.
So, does s/he know what s/he is talking about?
It is obvious s/he doesn’t know a first thing about budgeting. A good example is the text under the heading F-35 Upgrades. S/he seems to assume, that the budgeted $770m should be enough for all the future upgrades of the plane. In reality the budgeted amount tells you only how much money is allocated for the upgrades, not that there is an intention to purchase each and every upgrade that will be available. This alone takes out the credibility of the author. S/he obviously has no clue about how organizations plan spending and use money.
Second example is from the F-35 Base Costs. S/he is saying, that it would cost Finland $1bn extra to distribute the planes into four “satellite bases”. This is beyond ridiculous and shows that the writer does not actually know anything about how Finland operates its fighters.
The third example is from the Training. Again, the writer does not know anything about how air forces train their pilots and why they do it the way its done. And apparently s/he does not know that Norway was/is part of the F-35 project, and that has to do with the fact that they had number of pilots/planes at the Luke AFB.
As I said in an earlier comment, motivated reasoning stands out like a sore thumb from the analysis. I gave only three examples, but the fact of the matter is, the whole article is just one long chain of errors, biased assumptions, rumors, and obvious lack of even basic knowledge about the world. Even without the obvious lack of competence, biased motivations shine through from the language of the article:
No serious, self-respecting journalist would use terms like “the F-35 lobby” and “F-35 Fan Club” and phrases like “Defence Analysis hears more rumours”. Granted, serious journalist might cautiously mention rumors, but not without substantiating the credibility of the source. Not to mention that a serious journalist would check for spelling errors too.
The bottom line is, the writer of the so-called “analysis” could be as well a 15-yrs old kid in the basement of his/her grand-mother. Or, more likely, just another pathetic conspiracy theorist, who has too much time and very little thirst for unbiased knowledge. If you’re into conspiracies and/or hate F-35, by all means, go ahead and waste your time with this writer.
Perhaps the right way to go about it is to google the author of the article rather then the owner of the website. Not a know it all so just guessing.
Ok, I am not the right guy to verify this. But I would like to see you explain the Norwegian budget, not just in words, also in numbers.
Does anyone still truly believe Finland will choose something else than the F-35?
https://www.politico.com/newsletters/national-security-daily/2021/09/20/congress-to-white-house-finn-ish-the-sale-494403
“Finn-ish the deal”, they say. “We request the White House work closely with our Finnish partners to finalize this competition, and we ask that all departments and agencies be directed to fully support this effort.”
Note that all departments and agencies include the secret services, and fully supporting means using any and all means at their disposal, including blackmail, bribes, and even assassination. Not that they need to go that far. But it’s there.
America does not want any other outcome than the choice of the F-35, and it’s not like the other countries could match them for pressure. And this is particularly bad for the Boeing bid, because they can’t expect any support from a US negotiation team that is fully committed to achieve the victory of the F-35. Gripen, Typhoon, and Rafale may have a snowball’s chance in Hell because there’s no way small Euro countries can stand up to the US mastodon; but the Super Hornet doesn’t even have that.
Let’s just note that the F-35 is a strong contender, but it isn’t the current favourite in my book. We’ll see in a week or two.
https://www.iltalehti.fi/politiikka/a/8dfecfdf-e834-4f67-931d-ad255e54d3f4
So, what was he favorite in your book?
You don’t need to wait for so long.
Källor till IL: Amerikanska F-35 föreslås bli Flygvapnets nya jaktplan
https://www.iltalehti.fi/politiikka/a/8dfecfdf-e834-4f67-931d-ad255e54d3f4
Finland’s security idea is not build around USA-relationship, thus we can buy non-USA weapons and we have 5 competitors in the race and current political leadership would be very happy to acquire non-USA fighters. Any serious political pressure would backfire.
But of course Air Force staff is pro USA as we have operated USA-product for a long time. If something non-objective happens, it comes from this basic human psychology that also dictates why some never change car brand in their life.
“Any serious political pressure would backfire.”
No, not pressure from the USA. It’s a question of power dynamics. If an elephant applies pressure on a rabbit, it doesn’t backfire on the elephant.
Congrat FAF chosing F35!
Same sources that complained in Iltalehti sone weeks ago about their worries that politics seemed to favour Gripen in front of american fighter?
https://www.iltalehti.fi/politiikka/a/c81f63ee-9bf0-4139-a1d0-221a4d8510a8
Not strange at all. Samme thing happend in Norway before 2008. Saab and the Wallenberg family worked with quite a few people at the left side. Stein Ørnhøi from SV had to step aside from all things around the selection of a new plane when he was “taken with both hands in honey pot”
If true, this is a sad day for Saab. This pretty much means their fighter jet business is dead. Hopefully they realise this and shift their long term focus into robotics and AI instead. Maybe then, this turns out to be a blessing in disguise.
I can’t decide if the Finns are being realistic or naive here. It’s clearly a political decision to buy American. And as we have seen in recent years, US politics is extremely volatile and a huge part of the populous is supporting strong isolationistic tendencies. It’s also evident that the US is pivoting towards the Indo-Pacific and will leave Europe to handle Russia in the future.
So whatever guarantees the US has given today might very well mean something very different tomorrow.
I’m convinced the F-35 has some advanced and unique features, at the same time it’s obvious to me that the aircraft is extremely complicated and expensive to maintain.
Industrial cooperation, business offset and transfer of technology is probably a hard zero in this deal. This is not an investment, this will be a cost.
Basically the Finns took it up the ass. I get why, but it still hurts to see a brother bend over like that. But we’ve all done it, small nations sometimes have to.
Final conclusion: I’m dumping my Saab stock, they have underperformed for too long.
“It’s clearly a political decision to buy American.”
It is not. Clearly. The political decision is yet to be done. The information revealed were merely about rumors regarding the *recommendation* from the FDF. That is to say, FDF deems the F-35 the best fighter we can buy. FDF does not make political decisions. That’s prerogative of the government. The government can still decide for some other candidate (I very much doubt it, though).
I can understand why you’re disappointed, but refusing to accept the fact that F-35 won (if the information revealed by the news paper is correct) by its own merits and accusations of bending over are… I’m sorry to say, emotional BS, nothing more. Your guys lost because their product was inferior, admit it and get over it.
Yes, I’ll admit my wording was a bit crude and I will apologize for it. And yes, I’m disappointed. But mainly in Saab for botching yet another deal.
However, I did not say I thought Gripen was the superior product. I said I thought there are plenty of reasons to doubt the US claims of industrial offset or their will to defend Finland in the future.
If the F-35 is as good as some claim, I believe a mixed fleet of Swedish Gripen and Finnish F-35’s could actually become a more potent common air force than one with only Gripens.
That is if the risk of escalating cost of operating the F-35 doesn’t reduce the overall Finnish defence capacity. Which is far from certain…
@Svenska Kocken
I am not a snowflake, and I like heated debates – as long as the arguments remain rational – so there’s no need for apologies 🙂
I am not aware the U.S has made any promises to defend Finland in case we buy the HX fighter from there. Moreover, I am quite certain an informal promises – if such promises was ever even made – had absolutely no value in the decision process anyway. Talk is cheap and political leaders come and go. The HX decision makers are not that stupid to believe promises that can be reversed as the U.S leadership changes. No. Unless there is a secret, *formal* defense pact, which I very much doubt, this kind of promises did not play any role in the decision.
The industrial offset is another matter. In that regard the Saab offer was better, I agree. But as good as that part of the offer is/was, it is just a relatively small part of the whole deal.
“I believe a mixed fleet of Swedish Gripen and Finnish F-35’s could actually become a more potent common air force than one with only Gripens.” Again, agreed.
Saab apparently woke up relatively late to the value of 5th gen and deemed developing a genuine 5th gen fighter too risky and expensive. I believe the E/F model was a compromise – bring some of the 5th gen features to an existing plane instead of developing a completely new plane. Many people still don’t understand the fundamental change in thinking that 5th gen is all about and the value that comes along with this change. At the time Saab made that decision, the number of doubters was probably higher among the experts too. Besides, the Eurofighter consortium chose pretty much the same approach. So, I wouldn’t be too harsh on Saab for that decision. As they say, the hind sight is 20/20.
Saab views the computer calculation power as a paradigm shift in air warfare, not RCS reduction. Another is cost curve that they were able to halt. So making a totally new frame design was not seen as vital, from engineering point of view.
@corporal
Since I can do it on your recent article I put my comment here :
I think that the corporalfrisk article on simulation could be misreaden. CMANO proves above all that we don’t know how to interpret public data. Roughly speaking, on the basis of the data currently available to the general public and with a beginner’s use of the software, each of the aircraft used manages to do well against Russian units which are not necessarily to their advantage either.
Basically, if we disregard the names of the planes, there are still some very interesting things. What the game shows is that for example a medium range missile opens up interesting tactical possibilities if and only if you have the right detection capabilities. Also the carrying capacity of a stealth aircraft can be a major handicap in its use as well as the absence of a medium range missile. Another important element is that an interceptor with the qualities of the Eurofighter is a masterpiece in a diversified air force. The Thyphon / F-35 combo should not be taken lightly and I look at the coherence of the European air forces having this combo with another eye. In the same way the Rafale / M-2000 combo is very coherent … once again if we only take into account the public data.
But for a fighter with only one category of aircraft the attrition in case of intense conflict is still very fast.
In summary I hope that Dassault could drop some information to the HX team on the spectra.
Translated with http://www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)